|
Researchers from Microwave Devices and Integrated Circuits Department (Dept. No.4) of Institute of Microelectronics of Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMECAS) have succeed in developing 8-GS/s 4-bit ADC (analog-to-digital converter) and 10-GS/s 8-bit DAC (digital-to-analog converter) chips in mid-April.
The ADC based on flash-interpolating architecture, integrates about 1250 transistors. The ADC chip can work stably at a clock rate of 8 GS/s with a maximum of 9 GS/s.
The ultra-high-speed DAC based on R-2R current steering architecture, integrates about 1045 transistors, including a 10-Gbps built-in self-test generator. The DAC chip can work stably at a clock rate of 10 GS/s.
The ultra-high speed ADC/DAC chips play a key role in the fields of optical communication and broadband wireless communication. These 2 kinds of chips developed by IMECAS greatly increased the Maximum Sampling Rate of ADC/DAC chips in China, laying a solid foundation for the development of ADC/DAC circuits with higher performance.
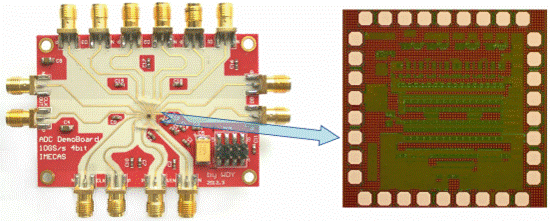
Fig.1 Evaluation Board (Left) and Photo (Right) of high-speed ADC Chip
(Image by IMECAS)
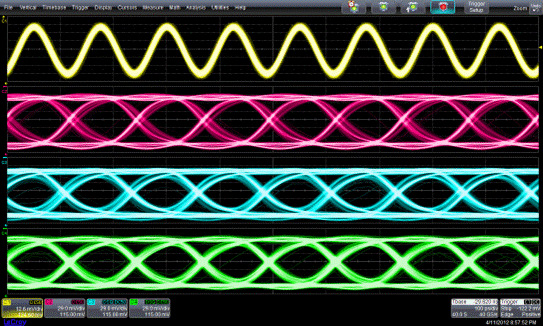
Fig.2: Eye diagrams of the clock signal, D0, D1 and D2 at a sample rate of 8 GS/s.
(Image by IMECAS)
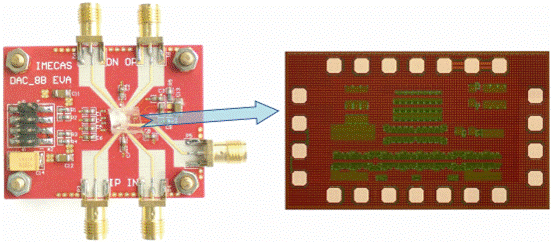
Fig.3 Evaluation Board (Left) and Photo (Right) of Ultra-high-speed DAC Chip
(Image by IMECAS)
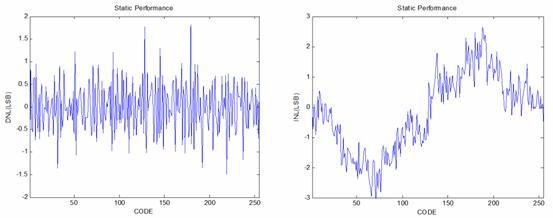
Fig.4 Experimental Results of Differential Non-Linearity (DNL) and Integral Non-Linearity (INL)
(Image by IMECAS)
CONTACT:
Researcher JIN Zhi
Institute of Microelectronics of Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail: jinzhi@ime.ac.cn
Website of Dept.:
http://english.ime.cas.cn/Research/ResearchDivisions/LAB4/
|














