SiC (Silicon Carbide) is the third-generation semiconductor materials. Because of its features such as wide band gap, high critical breakdown electric field and high load saturated density of particle flow, SiC has a predominant applicable value in military and astronautical field, especially in the photoelectric components with the properties of high temperature, high frequency and high power. It gradually replaces the components made from modern silicon and GaAs. Therefore, SiC power device, especially SiC MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) device, is the core technology of the next generation of high power electronic devices.
Recently, based on the 4-inch silicon technology platform, the SiC Power Devices Research Team at the Microwave Devices and Integrated Circuits Department of the Institute of Microelectronics of Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMECAS) developed 1200V/15A and 1700V/8A SiC MOSFET devices, which laid a solid foundation for the development of high-performance SiC power devices with Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) in the future.
Figure 2 is the characteristic curve of the 1200V/15A SiC MOSFET device. The output current is 10A when the VDS is 10V and the VGS is 22V and it's up to 15A when the VDS is 20V and the VGS is 22V. The reverse voltage is up to 1353V when the drain current is 100nA. Figure 3 is the characteristic curve of the 1700V/8A SiC MOSFET device. The output current is 5A when the VDS is 5V and the VGS is 22V and it's up to 8A when the VDS is 13V and the VGS is 22V. The reverse voltage is up to 1900V when the drain current is 20nA.
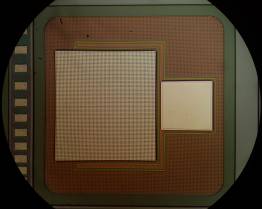
Figure 1: 1200V/15A、1700V/8A SiC MOSFET (Image by IMECAS)
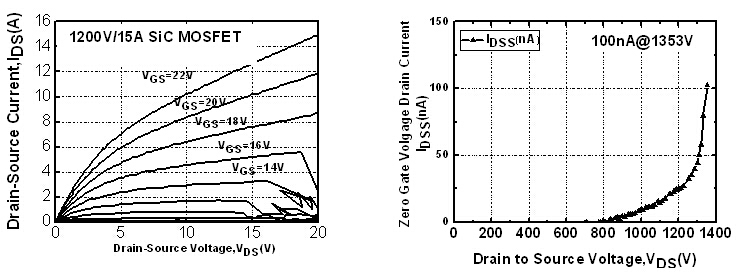
Figure 2: Characteristic Curve of the 1200V/15A SiC MOSFET Device (Image by IMECAS)
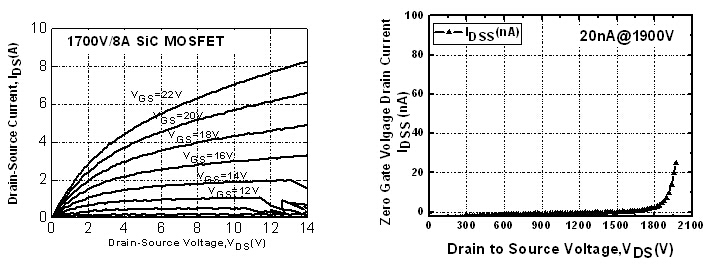
Figure 3: Characteristic Curve of the 1700V/8A SiC MOSFET Device (Image by IMECAS)














